Overview of Intelligent Waste Management Systems
Intelligent waste management systems are at the forefront of innovating urban waste solutions. These systems integrate smart technology to improve efficiency and sustainability in waste collection and processing. At their core, they encompass several components:
-
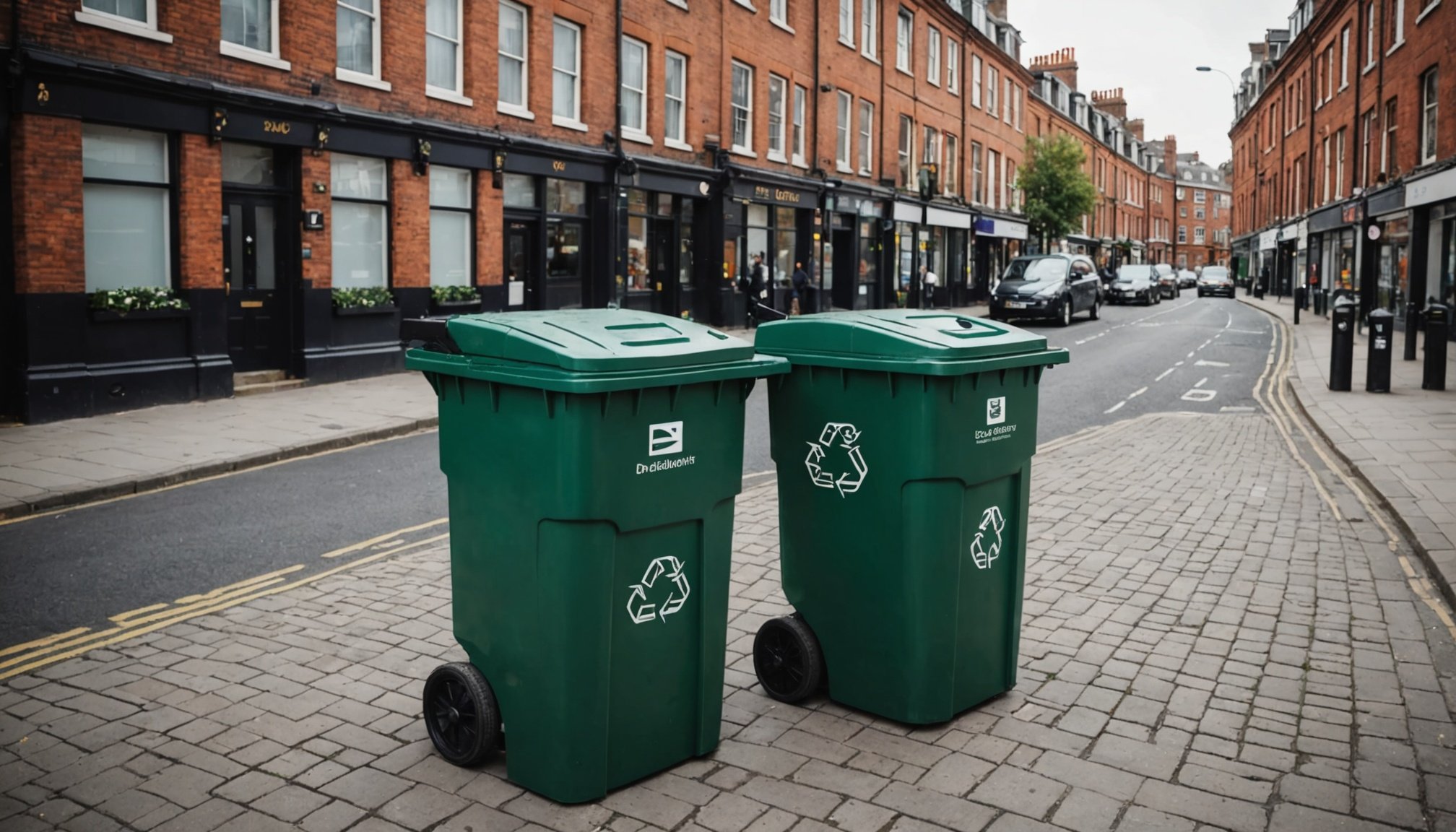
Sensors and IoT Devices: These are used to monitor waste levels in bins, ensuring timely collection and thereby reducing unnecessary pick-ups and fuel consumption.
Also read : Unveiling revolutionary innovations in precision agriculture revolutionizing potato farming across the uk
-
Data Analytics: Analyzing waste data helps in optimising routes and schedules, contributing to a more efficient collection process.
-
Communication Platforms: Residents can receive notifications about collection days or report issues, enhancing community engagement.
Also read : Captivating stories from asia: dive into diverse genres
Integrating technology into waste management is crucial for several reasons. It reduces operational costs, mitigates environmental impact through reduced carbon footprints, and boosts the efficiency of waste processing. Furthermore, these systems offer real-time data which assists in managing urban populations’ waste more effectively.
Currently, trends in smart waste solutions are heavily leaning towards AI integration, predictive analytics, and automation. As cities continue to grow, such innovations will be essential in managing urban waste efficiently, ensuring cities remain clean and sustainable for future generations. Maintaining a focus on intelligent solutions is not just a preference but a necessary evolution in the face of increasing urbanization.
Benefits of Intelligent Waste Management Systems
Integrating intelligent waste management systems brings numerous benefits. Foremost is the marked improvement in efficiency in waste collection and processing. By utilising smart technology, waste management entities can streamline their operations, ensuring waste is collected in a timely manner with optimised routes. This leads to a reduction in fuel usage and associated costs, further enhancing financial efficiency.
The sustainability implications of smart waste systems are equally significant. Reducing unnecessary emissions contributes to a lower carbon footprint, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change. Moreover, these systems encourage better waste segregation and recycling, diverting more waste from landfills and promoting a circular economy.
Urban residents also experience an enhanced quality of life with the deployment of intelligent solutions. Active community engagement, resulting from improved communication platforms, allows residents to be informed participants in waste management. Notifications about collection schedules and reporting mechanisms for waste-related issues ensure public convenience and responsiveness.
The benefits of smart waste systems thus extend beyond operational efficiencies to encompass environmental sustainability and improved urban living. By prioritising these systems, cities not only manage waste more effectively but also foster a cleaner and healthier environment for their residents, paving the way for future urban innovations.
Case Studies from UK Cities
Exploring real-world examples of UK waste management systems reveals the benefits and innovations in urban waste solutions. The case studies of London, Manchester, and Bristol exemplify successful implementation of smart technologies in addressing waste management challenges and fostering community engagement.
Case Study 1: London
London’s innovative approach includes smart bins equipped with sensors that indicate fill levels, reducing unnecessary collections. Data-driven route optimisation assists in managing operational costs and lowering emissions. The public response has been positive, with increased awareness about sustainable waste practices.
Case Study 2: Manchester
Manchester has delivered on adopting monitoring systems that enhance waste collection efficiency. Through community engagement initiatives, residents are actively involved in minimising waste and promoting recycling. The economic impact is notable, with evident cost savings and the redirection of funds toward city development projects.
Case Study 3: Bristol
Bristol stands out for its progressive use of technology, which includes smart waste systems characterised by IoT integrations. This fosters urban innovation, allowing for streamlined operations and improved public services. Community feedback highlights the system’s practicality and ease of use, encouraging broader adoption.
These case studies illustrate the positive impacts of smart waste systems, highlighting the UK as a leader in urban innovation. They underscore the importance of integrated approaches and indicate promising economic impacts through successful waste management systems.
Challenges in Implementing Smart Waste Solutions
Implementing smart waste solutions in urban areas presents a range of challenges. Financial and budgetary constraints are significant hurdles faced by city councils. The initial investment for intelligent waste management technologies can be substantial, necessitating careful financial planning and allocation of limited resources.
Existing infrastructures often present technical and operational challenges. Integrating new technologies requires updates to current waste management systems, which may not be compatible or equipped for modern innovations. This retrofit can be complex, demanding both technical expertise and persistent maintenance efforts to ensure systems run efficiently.
Resistance to change among stakeholders and residents further complicates the implementation of smart waste technologies. Community education and widespread advocacy are essential to address scepticism and to demonstrate the tangible benefits of smart technology. Engaging stakeholders early in the process can foster a collaborative approach, facilitating smoother adoption.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted strategy that involves engaging financial, technical, and social considerations. Overcoming these hurdles is critical for effective integration of urban waste solutions that enhance city functionality and well-being. Through strategic planning and clear communication, the pathway towards making cities more sustainable and efficient can be effectively navigated.
Future Trends in Waste Management
Technological advancements continue to shape the future of waste management, with AI and data analytics playing pivotal roles. These innovations allow for predictive analysis, enabling cities to anticipate waste patterns and adjust routes and collection schedules accordingly. As a result, cities can greatly increase their operational efficiency, improving response times and reducing costs.
One emerging trend is the utilisation of machine learning to refine recycling processes. By automating waste sorting, these systems can accurately identify and separate recyclable materials, reducing contamination rates and enhancing recycling efficacy. This not only ensures more materials are repurposed but also alleviates the burden on landfills.
Globally, cities like Amsterdam are models for integrated approaches combining technology with sustainable practices. These examples set benchmarks that influence UK waste management innovations. In projections, smart waste systems are expected to further integrate with urban infrastructure, becoming indispensable for city planning.
An essential element of evolving waste management is community involvement. Educational initiatives aim to align public interactions with technological advancements, fostering a collaborative environment. Through transparency and continued engagement, cities can ensure that future waste systems remain effective and broadly accepted. By embracing these trends, urban areas can progressively achieve greater ecological stewardship.